How Much Should You Water a Spider Plant?
Understanding Spider Plant Watering Needs
How much should you water a spider plant – Proper watering is crucial for a thriving spider plant. Several factors influence how often you need to water, ensuring your plant receives the right amount of moisture without overwatering or underwatering.
Factors Influencing Watering Frequency
The frequency of watering your spider plant depends on a combination of factors. These include the size of the pot, the type of soil, the season, the humidity level in your environment, and the location of the plant (indoors versus outdoors).
- Pot Size: Smaller pots dry out faster than larger ones, requiring more frequent watering.
- Soil Type: Well-draining soil allows excess water to escape, preventing root rot. Heavy, clay-based soils retain moisture longer, necessitating less frequent watering.
- Season: During warmer months (spring and summer), plants transpire more rapidly, requiring more frequent watering. In winter, watering needs decrease due to slower growth.
- Humidity: Higher humidity levels reduce the plant’s need for frequent watering, as the air already provides some moisture.
- Location: Plants in direct sunlight will dry out faster than those in shaded areas.
Signs of Underwatering and Overwatering
Recognizing the signs of both underwatering and overwatering is essential for maintaining a healthy spider plant. The following table summarizes the visual symptoms:
| Symptom | Underwatering | Overwatering |
|---|---|---|
| Soil | Dry and crumbly | Soggy and waterlogged |
| Leaves | Dry, brittle, and brown tips; drooping | Yellowing, wilting, and potentially mushy; may develop brown spots |
| Plant Appearance | Wilted and droopy | Leggy, weak growth; may exhibit root rot |
| Pot Drainage | Dry | Water standing in the saucer |
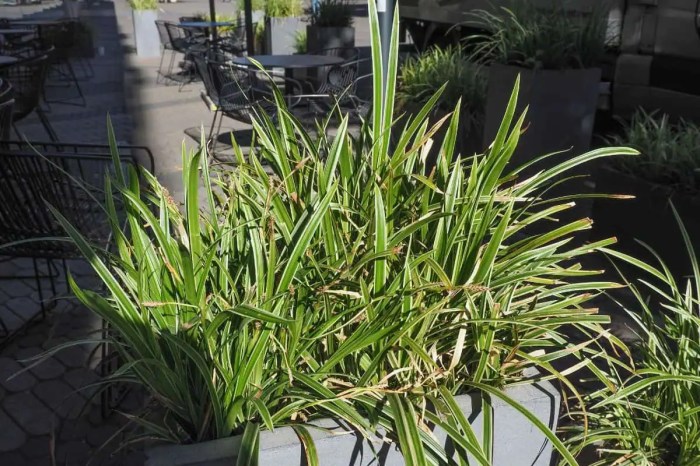
Checking Soil Moisture

Source: shortpixel.ai
Several methods can help you determine the soil moisture level before watering. The finger test is a simple and effective way to assess if your plant needs watering.
- Finger Test: Insert your finger about an inch into the soil. If the soil feels dry, it’s time to water. If it feels moist, wait a few more days.
- Moisture Meter: A moisture meter can provide a more precise reading of the soil’s moisture content.
- Weight Test: Lift the pot. A lighter pot indicates dry soil, while a heavier pot suggests moist soil.
Watering Frequency and Techniques: How Much Should You Water A Spider Plant
Establishing a consistent watering schedule is key to preventing both underwatering and overwatering. The best watering technique minimizes the risk of root rot and ensures even moisture distribution.
Watering Schedules Based on Environmental Conditions
Watering frequency varies depending on the environment. Indoor plants generally require less frequent watering than outdoor plants, particularly during the winter months.
- Indoor, Summer: Water thoroughly when the top inch of soil is dry, approximately once a week.
- Indoor, Winter: Water less frequently, perhaps every 2-3 weeks, depending on the indoor temperature and humidity.
- Outdoor, Summer: Water more frequently, possibly every few days, depending on sunlight and temperature.
- Outdoor, Winter: Reduce watering frequency significantly, depending on rainfall and temperature.
Watering Techniques
Both top watering and bottom watering have their advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right technique depends on your preferences and the specific needs of your plant.
- Top Watering: Pour water directly onto the soil surface until it drains from the drainage holes. This is the most common method.
- Bottom Watering: Place the pot in a tray of water and allow the soil to absorb water from the bottom up. This method is beneficial for preventing root rot.
Comparison of Watering Methods
Top watering is quicker and easier, but it can lead to uneven watering if not done carefully. Bottom watering ensures even moisture distribution but takes longer and may not be suitable for all pot types.
Soil and Potting Considerations
The right soil and pot size are crucial for healthy spider plant growth and appropriate watering.
Importance of Well-Draining Potting Mix
Well-draining soil is essential to prevent root rot. Avoid using heavy clay-based soils. Suitable potting mixes often include peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite.
Selecting the Right Pot Size
Choose a pot size appropriate for the plant’s size and root system. Overly large pots can lead to overwatering, while overly small pots can restrict growth.
Pot Material and Watering Frequency, How much should you water a spider plant
Terracotta pots are porous and allow for better air circulation, leading to faster drying. Plastic pots retain moisture longer, requiring less frequent watering.
Environmental Factors and Adjustments
Temperature, humidity, and light intensity all affect a spider plant’s water requirements.
Temperature and Humidity’s Influence
Higher temperatures and lower humidity levels increase transpiration, leading to increased watering needs. Conversely, cooler temperatures and higher humidity levels reduce watering frequency.
Seasonal Watering Adjustments
Watering frequency should be adjusted based on seasonal changes. Increase watering during warmer months and decrease it during cooler months.
Light Intensity’s Effect
Plants in bright, direct sunlight dry out faster than those in shade. Adjust watering frequency accordingly.
Troubleshooting Watering Issues
Addressing common watering problems promptly can prevent serious damage to your spider plant.
Solutions for Common Problems
Yellowing leaves can indicate overwatering or underwatering. Drooping leaves often signal underwatering. Root rot is a serious problem caused by overwatering.
Preventative Measures

Source: greengardencottage.com
Using well-draining soil, selecting the right pot size, and monitoring soil moisture levels are crucial preventative measures.
Reviving an Underwatered or Overwatered Plant
An underwatered plant can be revived by thoroughly watering it. An overwatered plant may require repotting into fresh, dry soil.
Visual Guide to Healthy Spider Plants
Healthy Spider Plant
A healthy, well-watered spider plant displays vibrant green leaves with a firm texture. The leaves are upright and not droopy, and the overall plant appearance is lush and full.
Watering a spider plant depends on several factors, including pot size and environmental conditions. Generally, allow the top inch of soil to dry out before watering thoroughly. To determine the optimal watering schedule, considering the increased frequency needed during warmer months is crucial; for guidance on this, check out this helpful article on how many times to water plants in summer.
Remember, overwatering is more harmful than underwatering for spider plants, so err on the side of caution.
Underwatered Spider Plant
An underwatered spider plant exhibits dry, brittle leaves with brown, crispy tips. The leaves are curled and droopy, and the overall plant appearance is wilted and stressed.
Overwatered Spider Plant
An overwatered spider plant shows yellowing or browning leaves that may be mushy or soft to the touch. The leaves may droop, and the overall plant may appear weak and leggy. The soil will be consistently soggy.
FAQ Corner
Can I use tap water to water my spider plant?
It’s best to use filtered or room-temperature tap water that has been allowed to sit out for 24 hours to allow chlorine to dissipate. Avoid using very cold water.
How often should I fertilize my spider plant?
Fertilize your spider plant during the growing season (spring and summer) with a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength, about every 2-4 weeks.
My spider plant’s leaves are turning brown. What should I do?
Brown leaves can indicate several issues, including overwatering, underwatering, or nutrient deficiency. Check the soil moisture, adjust your watering schedule accordingly, and consider using a balanced fertilizer.
How do I propagate spider plant babies (plantlets)?
Once the plantlets develop roots, you can gently detach them from the mother plant and pot them in their own containers with well-draining soil.