How Much Does a Water Desalination Plant Cost?
Factors Influencing Desalination Plant Costs
How much does a water desalination plant cost – The cost of building a desalination plant is a complex issue influenced by a multitude of factors. These factors interact in intricate ways, making accurate cost prediction challenging. However, understanding these key variables allows for a more informed assessment of potential project expenses.
Plant Capacity and Technology Selection
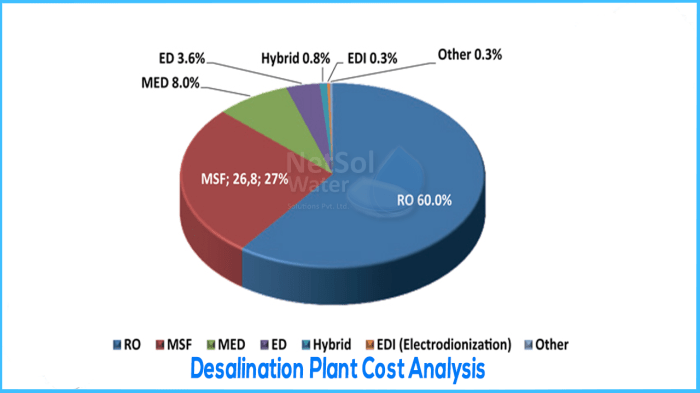
The daily water production capacity significantly impacts overall costs. Larger plants generally benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower costs per unit of treated water. However, this relationship isn’t strictly linear; incremental cost reductions diminish as plant size increases. Different desalination technologies also contribute to cost variations. Reverse osmosis (RO) is typically less expensive to build than multi-stage flash distillation (MSF), but operational costs may differ significantly based on energy consumption and chemical requirements.
Land Acquisition and Site Preparation
Securing suitable land near a water source is crucial. Coastal locations are preferred for seawater desalination, but land prices and availability can vary drastically depending on location and proximity to infrastructure. Site preparation costs, including land leveling, utility connections, and environmental remediation, add substantial expense to the project.
Infrastructure Requirements
Significant investment is needed for essential infrastructure, including pipelines for transporting both raw and treated water, and a reliable power supply. The length and complexity of these pipelines, along with the power source (e.g., grid connection versus on-site generation), directly impact infrastructure costs. Power requirements are particularly significant for energy-intensive technologies like MSF.
Environmental Regulations and Permitting
Environmental regulations and permitting processes add considerable time and expense to desalination projects. Compliance with environmental impact assessments, discharge permits, and other regulatory requirements can significantly increase project costs and timelines. The complexity of these processes varies greatly by location and jurisdiction.
Cost Comparison Table, How much does a water desalination plant cost
| Technology | Capital Cost (USD/m³/day) | Operational Cost (USD/m³/day) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse Osmosis (RO) | 1000-3000 | 0.30-1.00 | Lower capital cost, higher energy consumption in some cases |
| Multi-Stage Flash Distillation (MSF) | 3000-5000 | 0.20-0.80 | Higher capital cost, potentially lower energy consumption depending on design and fuel costs |
| Multi-Effect Distillation (MED) | 2500-4500 | 0.25-0.90 | Moderate capital cost, relatively low energy consumption |
| Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR) | 2000-4000 | 0.40-1.20 | Suitable for brackish water, moderate energy consumption |
Breakdown of Capital Costs: How Much Does A Water Desalination Plant Cost
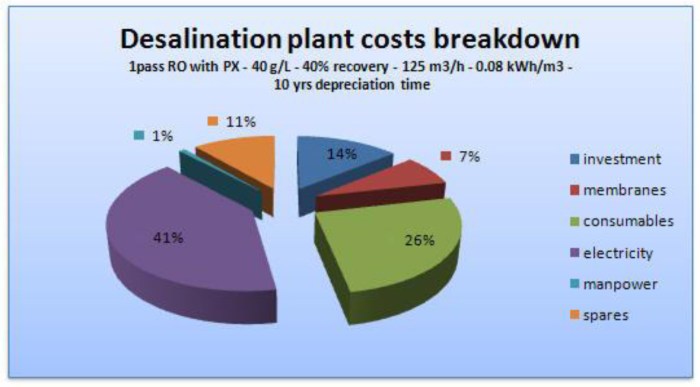
Capital expenditure (CAPEX) for a desalination plant encompasses various significant components. A thorough understanding of these components is essential for accurate budgeting and project planning. Cost overruns are a common concern, and proactive mitigation strategies are crucial.
Major CAPEX Components
Major components contributing to CAPEX include the cost of procuring and installing desalination equipment (membranes, pumps, heat exchangers, etc.), constructing plant buildings and facilities (intake structures, pretreatment units, product water storage tanks), and the aforementioned infrastructure needs (pipelines, power supply). Engineering and design fees, as well as project management costs, also contribute significantly.
Equipment Procurement and Installation
The cost of desalination equipment varies depending on technology, capacity, and vendor. Installation costs include labor, site preparation, and testing. The complexity of the equipment and the need for specialized expertise can significantly impact installation expenses.
Plant Construction and Facilities
Construction costs depend on factors such as building materials, labor rates, and site conditions. The design of the plant’s buildings and facilities, including safety features and environmental considerations, also influence construction expenses.
The cost of a water desalination plant varies wildly depending on size and technology, ranging from millions to billions of dollars. This significant investment highlights the importance of efficient water management, which brings to mind another type of resource management: learning how many times to water rosemary plant to optimize its growth. Ultimately, both efficient water use and large-scale desalination projects are crucial for addressing global water scarcity.
Cost Overruns and Mitigation
- Unforeseen Site Conditions: Unexpected geological challenges or environmental factors can lead to delays and cost overruns. Thorough site investigations and contingency planning are crucial.
- Equipment Delays: Delays in equipment delivery can disrupt the project schedule and increase costs. Careful vendor selection and contract management are essential.
- Changes in Design or Specifications: Changes during construction can lead to cost overruns. A well-defined design and a robust change management process are needed.
Economies of Scale
Larger desalination plants generally achieve lower costs per unit of treated water due to economies of scale. This is because fixed costs (e.g., engineering, permitting) are spread over a larger production volume. However, the marginal cost reduction diminishes as plant size increases.
Operational and Maintenance Expenses
Ongoing operational and maintenance (O&M) expenses represent a significant portion of the total lifecycle cost of a desalination plant. Careful planning and efficient operation are essential for minimizing these costs.
Ongoing Operational Costs
Operational costs include energy consumption (a major expense, particularly for energy-intensive technologies), chemical usage (for pretreatment and cleaning), labor (operators, maintenance personnel), and administrative expenses.
Maintenance Schedules and Costs
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring plant reliability and efficiency. This includes scheduled inspections, cleaning, repairs, and component replacements. A well-defined maintenance plan is essential for minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of equipment.
Water Quality and Pretreatment
Source: netsolwater.com
Water quality significantly impacts operational expenses. High levels of fouling or scaling can reduce membrane performance, increase energy consumption, and necessitate more frequent cleaning. Effective pretreatment is crucial for minimizing these impacts.
Cost Minimization Strategies
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Implementing energy-efficient technologies and optimizing plant operations can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Optimized Chemical Usage: Careful monitoring and control of chemical usage can reduce chemical costs without compromising water quality.
- Preventative Maintenance: A proactive maintenance program can prevent costly repairs and extend the lifespan of equipment.
Lifecycle Cost Model
A lifecycle cost model considers all costs associated with a desalination plant over its entire operational life, including CAPEX, O&M expenses, and potential decommissioning costs. This model helps in making informed decisions about plant design, technology selection, and operation strategies. A simple model might involve projecting annual O&M costs based on historical data or industry benchmarks and discounting these costs to present value.
More sophisticated models can incorporate probabilistic factors to account for uncertainty in cost estimates.
Geographic Location and its Impact
The geographical location of a desalination plant significantly influences its cost. Factors such as climate, labor costs, and material availability interact to determine overall project expenses. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for optimizing project cost-effectiveness.
Coastal vs. Inland Locations
Coastal locations are generally preferred for seawater desalination due to proximity to the water source. However, land costs and infrastructure availability can be significantly higher in coastal areas compared to inland locations. Inland plants often require extensive pipeline infrastructure to transport water to the point of use.
Labor Costs and Material Availability
Local labor costs and the availability of construction materials influence project expenses. Regions with high labor costs or limited access to construction materials may experience higher project costs. Utilizing locally sourced materials can reduce transportation costs and support local economies.
Climate and Environmental Conditions
Climate and environmental conditions affect plant design and construction costs. Harsh weather conditions may require more robust construction techniques and increase construction time. Extreme temperatures can also affect energy consumption and maintenance requirements.
Cost Savings from Local Resources
Utilizing locally sourced materials and labor can lead to significant cost savings. This reduces transportation costs and supports local businesses. However, the availability and quality of local resources must be carefully evaluated.
Key Geographic Factors

Source: yale.edu
- Proximity to water source
- Land costs and availability
- Local labor costs
- Availability of construction materials
- Climate and environmental conditions
- Infrastructure availability
Financial Considerations and Funding
Source: knepublishing.com
Securing adequate funding and managing financial risks are crucial for successful desalination projects. Various funding models exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Careful financial planning and risk assessment are essential for project success.
Funding Models
Desalination projects can be funded through various models, including public funding, private investment, and public-private partnerships (PPPs). PPPs combine the strengths of both public and private sectors, sharing risks and responsibilities. The chosen model significantly impacts project financing costs and risk allocation.
Financing Costs
Financing costs, such as interest rates and loan repayment schedules, significantly influence the overall project budget. Securing favorable financing terms is crucial for minimizing project costs.
Permitting and Licensing
Obtaining necessary permits and licenses is a critical step in the project development process. The permitting process can be lengthy and complex, requiring significant time and resources.
Successful and Unsuccessful Projects
Analyzing successful and unsuccessful desalination projects provides valuable insights into best practices and potential pitfalls. Successful projects typically involve thorough planning, effective risk management, and strong stakeholder engagement. Unsuccessful projects often suffer from inadequate planning, cost overruns, or operational challenges.
Hypothetical Financial Projections
A hypothetical 20-year financial projection for a desalination plant would involve estimating CAPEX, O&M costs, water sales revenue, and financing costs. This projection would allow for an assessment of project profitability and financial viability. The specific numbers would depend heavily on the plant’s size, technology, location, and financing terms. For example, a 100,000 m³/day RO plant might have a CAPEX of $100 million, annual O&M costs of $5 million, and annual revenue of $15 million, leading to positive cash flow after a few years, assuming a reasonable water price and financing structure.
However, unexpected events like equipment failures or changes in water demand could significantly alter these projections.
Top FAQs
What are the typical lifespan and depreciation rates of desalination plant components?
Lifespans vary greatly depending on the component and technology. Major components like membranes might last 5-10 years, while structural elements have much longer lifespans. Depreciation rates are calculated based on these lifespans and accounting standards.
How does insurance affect the overall cost of a desalination plant?
Insurance premiums are a significant ongoing expense, covering potential damage from natural disasters, equipment malfunction, and liability. The cost depends on factors like plant location, technology, and the insurer’s risk assessment.
Are there government subsidies or incentives available for desalination projects?
Many governments offer incentives, including tax breaks, grants, and low-interest loans, to encourage the development of desalination projects, particularly in water-stressed regions. Specific programs vary by location.