How Much Should I Water Plants?
Understanding Your Plants’ Water Needs
How much should i water plants – Proper watering is crucial for healthy plant growth. A plant’s water requirements are influenced by several key factors, understanding which is vital for successful plant care. These factors interact to determine how frequently and how much water your plants need.
Factors Influencing Plant Water Requirements
Several factors influence how much water a plant needs. These include sunlight exposure, soil type, pot size, and the plant’s species.
- Sunlight: Plants in direct sunlight dry out faster than those in shade, requiring more frequent watering.
- Soil Type: Different soils retain varying amounts of water. Sandy soils drain quickly, while clay soils retain water for longer periods.
- Pot Size: Smaller pots dry out more quickly than larger ones, necessitating more frequent watering for smaller containers.
- Plant Type: Different plant species have different water requirements. Succulents, for instance, need less frequent watering than ferns.
Soil Types and Water Retention
Understanding soil types and their water retention properties is essential for proper watering. The table below provides a comparison of different soil types.
| Soil Type | Water Retention | Drainage | Suitable Plants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy | Low | Excellent | Cacti, succulents |
| Clay | High | Poor | Water-loving plants like ferns and hostas |
| Loamy | Moderate | Good | A wide variety of plants |
| Peaty | High | Poor to Moderate | Acid-loving plants like blueberries and rhododendrons |
Examples of Plants with Varying Water Needs
Here are some examples of plants with high, medium, and low water requirements:
- High-Water Plants: Ferns, calatheas, peace lilies
- Medium-Water Plants: Snake plants, pothos, spider plants
- Low-Water Plants: Cacti, succulents, aloe vera
Watering Techniques
Employing the correct watering technique is just as important as knowing how often to water. Different methods cater to different plant needs and soil types.
Proper Watering Methods
There are several effective ways to water your plants, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Determining how much water your plants need depends on several factors, including the type of plant, pot size, and environmental conditions. A crucial aspect to consider is frequency; to understand this better, check out this helpful guide on how many times should water plants. Ultimately, the amount of water should be enough to moisten the soil thoroughly, but avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
- Top Watering: This involves pouring water directly onto the soil surface. It’s simple but can lead to surface runoff if done improperly.
- Bottom Watering: This method involves placing the pot in a tray of water, allowing the soil to absorb moisture from the bottom up. This is beneficial for plants that don’t like their leaves wet.
- Deep Watering: This involves watering thoroughly until water drains out of the drainage holes. This ensures the roots are fully saturated.
Signs of Underwatering and Overwatering
Recognizing the signs of underwatering and overwatering is crucial for preventing plant damage.
- Underwatering: Wilting leaves, dry soil, brittle stems, leaf browning or yellowing (starting from the edges)
- Overwatering: Yellowing leaves (starting from the bottom), soggy soil, root rot (indicated by a foul odor from the soil), stunted growth.
A Simple Watering Schedule

Source: exactdn.com
A flexible watering schedule is best, adjusted according to the plant’s needs and environmental conditions. Generally, high-water plants may need watering every 2-3 days, medium-water plants every 5-7 days, and low-water plants every 1-2 weeks. However, always check the soil moisture before watering.
Tools and Equipment
The right tools can make watering easier and more effective. From watering cans to automatic systems, there’s a range of options available.
Types of Watering Cans
Various watering cans cater to different needs. Rose-head watering cans provide gentle watering, while long-spout cans reach deeper into pots. The size of the can should be appropriate for the number and size of your plants.
Automatic Watering Systems
Automatic watering systems offer convenience but can be costly to install and maintain. They are particularly useful for those who travel frequently or have a large number of plants. However, malfunctions can lead to overwatering.
DIY Self-Watering Systems
A simple self-watering system can be created using readily available materials such as plastic bottles, wicks (cotton rope or fabric strips), and pots with drainage holes. The design involves placing a water reservoir (e.g., a plastic bottle filled with water) inside or near the plant pot, with the wick drawing water from the reservoir into the soil.
Environmental Factors: How Much Should I Water Plants
Environmental conditions significantly impact a plant’s water needs. Adjusting your watering schedule based on these factors is crucial for optimal plant health.
Impact of Temperature, Humidity, and Sunlight
Higher temperatures and lower humidity increase evaporation rates, requiring more frequent watering. Similarly, plants in direct sunlight dry out faster than those in shade.
Seasonal Changes and Watering Adjustments
Watering frequency should be adjusted according to seasonal changes. During hotter, drier months, plants require more frequent watering, while during cooler, wetter months, watering frequency can be reduced.
Environmental Factors and Watering Frequency
| Season | Temperature | Humidity | Watering Frequency Adjustment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | High | Low | Increase frequency |
| Winter | Low | High | Decrease frequency |
| Spring | Moderate | Moderate | Gradually increase frequency |
| Autumn | Moderate | Moderate | Gradually decrease frequency |
Troubleshooting Watering Problems
Improper watering can lead to various plant problems. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing irreversible damage.
Common Watering Problems and Solutions
Common problems include wilting, yellowing leaves, and root rot. Solutions range from adjusting watering frequency to repotting the plant.
Reviving Underwatered or Overwatered Plants

Source: co.uk
Underwatered plants can often be revived by thorough deep watering. Overwatered plants may require repotting in fresh, well-draining soil to prevent root rot.
Flowchart for Diagnosing Watering Issues
A flowchart can help systematically diagnose and treat watering-related problems. The flowchart would begin with assessing the visible symptoms (wilting, yellowing, etc.), leading to a determination of underwatering or overwatering, and finally, to the appropriate treatment (more frequent watering, less frequent watering, repotting).
Specific Plant Examples
Watering requirements vary greatly between plant species. Here’s a closer look at some common houseplants.
Watering Schedules for Common Houseplants
- Succulents: Water thoroughly only when the soil is completely dry, usually every 2-3 weeks. Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings to prevent root rot.
- Ferns: Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Water more frequently during dry periods or when the top inch of soil feels dry.
- Snake Plants: Water sparingly, allowing the soil to dry out completely between waterings. Overwatering is a common problem with snake plants.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Plant Watering
Outdoor plants generally require more frequent watering than indoor plants due to higher evaporation rates caused by sun, wind, and heat. Indoor plants are sheltered from these factors.
Container vs. In-Ground Planting, How much should i water plants
Plants in containers dry out more quickly than those planted directly in the ground. This is because the soil in containers has a smaller volume and is exposed to more air circulation. Consequently, container plants require more frequent watering.
Visual Aids
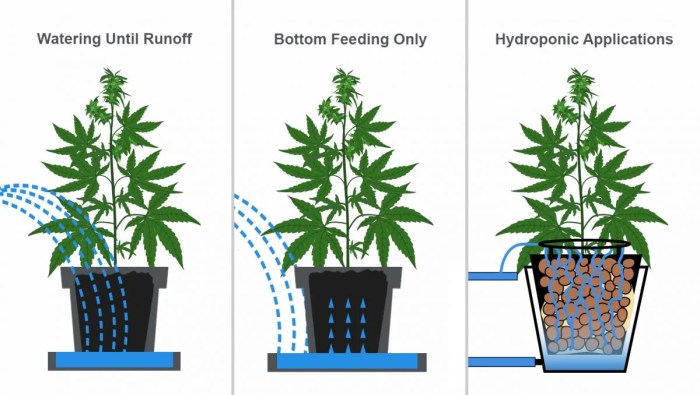
Source: 2fast4buds.com
Visual cues are essential for determining a plant’s hydration status. Observing leaf appearance, soil condition, and overall plant health provides valuable insights.
Visual Cues of Proper, Under, and Overwatering
A properly watered plant will have firm, turgid leaves, moist but not soggy soil, and a healthy, vibrant appearance. An underwatered plant will exhibit wilting leaves, dry and cracked soil, and a generally droopy appearance. An overwatered plant will display yellowing lower leaves, soggy soil, and potentially stunted growth. The soil may even have a foul odor indicating root rot.
Determining When to Water
To determine if a plant needs watering, check the soil moisture by inserting your finger about an inch into the soil. If the soil feels dry, it’s time to water. Another method is to use a moisture meter, which provides a more precise measurement of soil moisture.
User Queries
What are the signs of root rot?
Root rot manifests as wilting, yellowing leaves, and a foul odor emanating from the soil. The soil itself may be soggy and dark.
How often should I check my plants’ soil moisture?
It’s best to check the soil moisture daily, especially for plants in smaller pots or those in sunny locations. Use your finger to check the top inch or two of soil.
Can I use tap water to water my plants?
Generally, yes, but tap water may contain chemicals or minerals that could harm some plants. Letting tap water sit out overnight to allow chlorine to dissipate is recommended.
My plant is drooping, is it underwatered or overwatered?
Drooping can be a sign of both. Check the soil; if it’s dry, it’s underwatered. If it’s soggy, it’s likely overwatered. Examine the leaves for other symptoms to help determine the cause.