Gatorade G2 Ingredients & Macronutrient Profile

Nutrition facts of gatorade g2 – Gatorade G2 is a low-calorie sports drink marketed as a hydration and electrolyte replenishment beverage. Understanding its ingredient list and macronutrient profile is crucial for assessing its suitability within various dietary contexts. This section provides a detailed analysis of both aspects.
Ingredient Breakdown of Gatorade G2
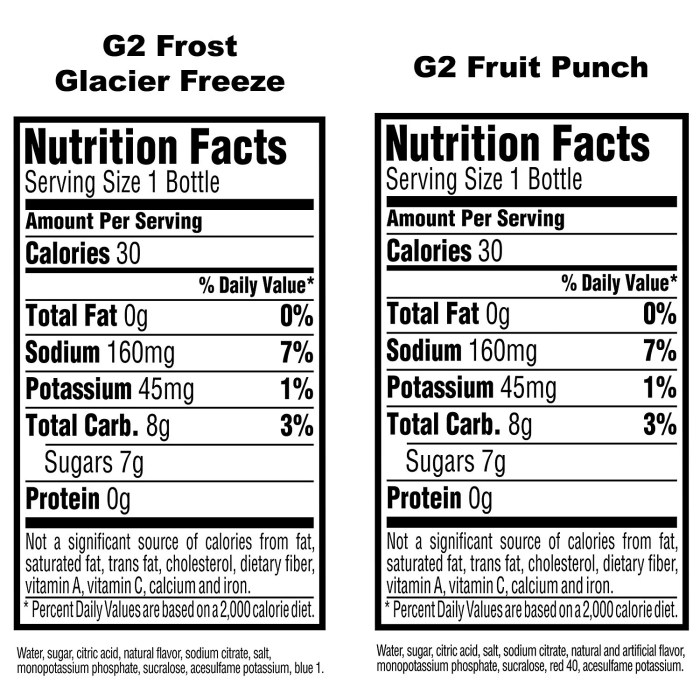
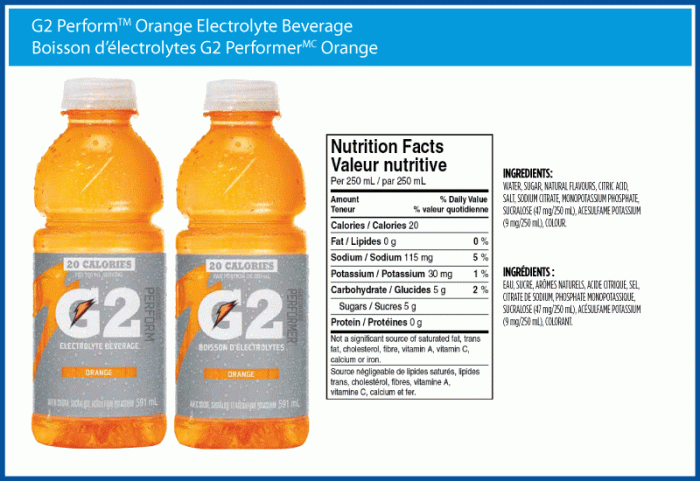
The exact ingredient list and quantities can vary slightly depending on flavor, but a typical serving of Gatorade G2 contains water, sucrose, citric acid, natural and artificial flavors, salt, sodium citrate, monopotassium phosphate, gum arabic, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, sucralose, acesulfame potassium, and colors (including Red 40, Blue 1, and Yellow 5, depending on the flavor). The quantities of each ingredient are proprietary information not publicly released by the manufacturer in full detail.
However, the nutritional information label provides a summary of the macronutrient content. The presence of artificial sweeteners like sucralose and acesulfame potassium contributes to the low-calorie profile of G2 compared to its original counterpart. The electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium) are included to aid in rehydration after physical activity.
Macronutrient Composition of Gatorade G2
Gatorade G2 is designed to be a low-carbohydrate option compared to other sports drinks. This is achieved primarily through the use of artificial sweeteners and a reduced amount of sucrose. The following table provides a typical macronutrient profile per serving (usually 20 fluid ounces), though slight variations can occur based on the specific flavor and manufacturing batch. It’s important to always refer to the nutrition label on the specific product purchased for the most accurate information.
| Macronutrient | Quantity per Serving (approx.) | Units | Percentage of Daily Value (%DV) (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 10-14 | grams | 4-6% |
| Protein | 0 | grams | 0% |
| Fat | 0 | grams | 0% |
| Total Calories | 40-60 | calories | – |
Micronutrient Content of Gatorade G2
Gatorade G2, marketed as a lower-calorie sports drink, contains a blend of vitamins and minerals intended to replenish electrolytes and support hydration during or after physical activity. However, the specific micronutrient profile and its significance relative to overall health and dietary needs require careful examination. The amounts present are relatively modest compared to recommended daily intakes, highlighting its role as a supplemental, rather than primary, source of these essential nutrients.Gatorade G2 provides a small amount of several vitamins and minerals.
A typical serving (591ml) contains vitamins such as Vitamin B3 (niacin), Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), and Vitamin B12 (cobalamin), along with minerals like potassium and sodium. Precise quantities vary slightly depending on the flavor but generally remain within a narrow range. For example, a serving might contain approximately 10% of the recommended daily intake of Vitamin B3 and smaller percentages of other vitamins and minerals.
The exact values should be checked on the product label as formulations can change.
Gatorade G2, with its lower sugar content, offers a refreshing hydration option for athletes. But for those seeking a protein boost alongside their electrolytes, consider the nutritional profile of cottage cheese nutrition facts , a surprisingly versatile post-workout snack. Returning to Gatorade G2, remember to check the serving size for accurate nutritional information, as it can impact your overall intake.
Comparison of Micronutrient Content to Other Sports Drinks and Recommended Daily Intakes
The micronutrient content of Gatorade G2 is comparable to other commercially available sports drinks, many of which also include small amounts of vitamins and minerals. However, the amounts are generally significantly lower than those found in a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Direct comparisons require referencing the specific nutritional information provided by each competing brand.
It is crucial to understand that Gatorade G2 is designed to replenish fluids and electrolytes lost during exercise, not to serve as a primary source of vitamins and minerals. Relying solely on sports drinks for micronutrient intake would likely lead to deficiencies in many essential nutrients. For instance, a serving of Gatorade G2 provides a fraction of the recommended daily intake of Vitamin C, which is crucial for immune function and antioxidant protection, a nutrient notably absent from most sports drinks.
Potential Health Benefits and Drawbacks Associated with the Micronutrient Profile
The micronutrients in Gatorade G2, while present in small amounts, offer potential benefits. These benefits are, however, modest and are secondary to the drink’s primary function of hydration and electrolyte replenishment.
- Potential Benefits: The small amounts of B vitamins can contribute to energy metabolism and nerve function. Potassium contributes to maintaining healthy blood pressure. However, these contributions are minimal and should not be relied upon as a significant source of these nutrients.
- Potential Drawbacks: The added sugars and relatively low micronutrient content mean that relying on Gatorade G2 as a primary source of nutrition is detrimental. Overconsumption can lead to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and other health problems associated with high sugar intake. The limited range of micronutrients present further underscores the need for a balanced diet to meet overall nutritional requirements.
The high sodium content can also be problematic for individuals with hypertension or other sodium-sensitive conditions.
Potential Health Implications of Regular Gatorade G2 Consumption: Nutrition Facts Of Gatorade G2
Regular consumption of Gatorade G2, while offering hydration and electrolyte replenishment, presents potential long-term health implications primarily due to its sugar content and overall caloric contribution. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed choices about its inclusion in a balanced diet. The following sections detail the potential effects on various aspects of health.
Impact of High Sugar Intake, Nutrition facts of gatorade g2
Gatorade G2, despite being a lower-sugar option compared to its original counterpart, still contains a significant amount of sugar. Chronic high sugar intake is linked to various health problems. The added sugars in G2 contribute to increased caloric intake, potentially leading to weight gain and an elevated risk of developing metabolic syndrome, characterized by a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol or triglyceride levels.
Furthermore, excessive fructose consumption, a component of the sugar in G2, has been associated with increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The body processes fructose differently than glucose, potentially overloading the liver and contributing to fat accumulation. These effects are exacerbated by regular consumption over extended periods. For instance, a person consuming two bottles of G2 daily would significantly exceed recommended daily sugar intake levels, increasing their risk of these conditions.
Effects on Dental Health
The sugar content in Gatorade G2 creates a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to dental caries (cavities) and increased susceptibility to gum disease. The frequent consumption of sugary drinks, including G2, throughout the day, especially without proper oral hygiene, significantly increases this risk. The acidic nature of the beverage further contributes to enamel erosion, even without the presence of bacteria.
This is especially relevant for individuals who regularly consume G2 between meals, allowing prolonged exposure of teeth to the acidic environment.
Influence on Weight Management
Regular consumption of Gatorade G2 can hinder weight management efforts. The added sugars and carbohydrates provide a substantial caloric load, which, if not balanced by sufficient physical activity and a calorie-controlled diet, contributes to weight gain. The caloric density of G2, while lower than other sports drinks, still surpasses that of plain water. Even seemingly small amounts consumed regularly can accumulate, impacting overall energy balance and potentially leading to obesity over time.
For example, a daily intake of two bottles of G2 can add approximately 200-300 extra calories to a person’s daily diet, which is significant when considering the small caloric deficits needed for sustainable weight loss.
Summary of Potential Health Implications and Recommended Consumption Frequency
The following points summarize the potential negative health consequences of regular Gatorade G2 consumption and provide guidelines for appropriate usage:
- Increased risk of weight gain and obesity due to added sugars and calories.
- Elevated risk of developing metabolic syndrome, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) due to fructose content.
- Increased risk of dental caries and gum disease due to sugar’s effect on oral bacteria.
- Potential for dehydration if not consumed in conjunction with adequate water intake.
It is recommended to limit Gatorade G2 consumption to situations of intense physical activity requiring electrolyte replenishment and to prioritize water as the primary hydration source. Occasional use should not pose significant health risks, but regular, frequent consumption should be avoided. The best approach is to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice based on individual health needs and activity levels.
User Queries
Is Gatorade G2 suitable for diabetics?
Because of its sugar content, Gatorade G2 should be consumed cautiously by diabetics. Consult your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.
Can I use Gatorade G2 as a daily replacement for water?
No, water is the best choice for daily hydration. Gatorade G2 is best suited for replenishing electrolytes lost during intense physical activity.
Does Gatorade G2 contain artificial sweeteners?
This varies depending on the specific Gatorade G2 flavor. Check the ingredient list on the packaging for specific information.
What are the best alternatives to Gatorade G2 for hydration?
Water is always the best option. Other alternatives include coconut water (for electrolytes) or diluted fruit juice (for natural sugars).
